Ambient Air Monitoring for Methyl Bromide in West Long Beach
Contact
I-click dito upang tingnan ang pahinang ito sa Tagalog.
ចុចទីនេះដើម្បីមើលទំព័រនេះជាភាសាខ្មែរ
Haga clic aquí para ver esta página en español.
Review January 30th meeting presentation and recordings
CARB and the agencies listed below hosted a public meeting on January 30th, 2025, from 6 pm to 8 pm. The meeting was held at The Salvation Army Long Beach Red Shield Chapel and online via Zoom. Video recordings and PDF presentations for the public meeting are available in English, Español, Tagalog, and ខ្មែរ. Please email CommunityAir@arb.ca.gov with questions or for more information.
Overview
Methyl Bromide (MeBr) is a colorless, odorless pesticide used to fumigate agricultural products for insect pests to protect public health and to meet international import and export standards. In 2023, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) began monitoring outside air for concentrations of methyl bromide in the community near Hudson Park in West Long Beach. The monitoring detected elevated levels of methyl bromide during the spring months. In 2024, CARB convened an interagency working group to assess the potential risk to the community and address sources of MeBr.
In January 2025, the two facilities that are likely responsible for these elevated concentrations agreed to additional conditions that will address the levels of MeBr. These additional conditions are included in, and now required as part of, the restricted materials permits issued to the facilities by the Los Angeles County Agricultural Commissioner (LA CAC). CARB will continue to monitor MeBr concentrations near the sources to measure and track the effectiveness of the facility improvements. Current MeBr air monitoring data is available below.
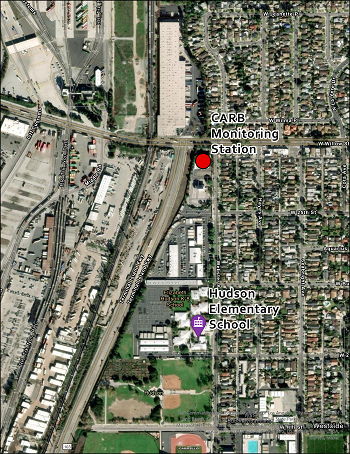
Why did CARB decide to monitor for MeBr?
During a community tour of the Long Beach area in 2019, CARB heard concerns expressed about MeBr fumigation operations near residential neighborhoods. In response, CARB reviewed available background information, including data from the South Coast AQMD Multiple Air Toxics Exposure Study, to identify potential locations for air monitoring. When new MeBr air monitoring technology became available, CARB established a temporary air monitoring site (identified on the map) to measure MeBr concentrations in the AB 617 community of Wilmington, Carson and West Long Beach beginning on January 12, 2023. The monitoring site is located just north of Hudson Elementary School in Long Beach and was chosen because it is downwind of two fumigation facilities.
What were the findings from CARB’s MeBr monitoring?
The air monitor measures MeBr concentrations which are compared to the health-based Reference Exposure Levels (REL) set by California’s Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA). A REL is the amount of a chemical in the air that people can be exposed to without expecting any harmful noncancer health effects. These levels consider sensitive groups like infants and children.
There are two types of RELs that were considered when reviewing this data: The acute REL, which is the health protective level for 1-hour exposures and the chronic REL, which is the health protective level for continuous exposure over a long period, such as a year or more. The air monitoring results found:
- There were two hourly measurements of MeBr at the air monitoring site that approached the acute REL of 1,000 ppb, which were 983 and 966 ppb on February 29 and March 5, 2024.
- Between January 12, 2023, and April 30, 2024, the average concentration of MeBr was 2.1 parts per billion (ppb) at the monitoring site, which is above the OEHHA chronic REL of 1 ppb.
- Elevated concentrations were usually observed between 6 pm and 11 pm and these events were most common between early February and late April in 2023 and 2024.
Effective May 20, 2025, CARB has transferred primary monitoring and data reporting responsibilities to South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD). Current monitoring data can be found on SCAQMD’s website here. Legacy data from January 2023 through May 2025 will continue to be available for download on CARB’s AQView data portal. CARB will continue to collaborate and support SCAQMD in their monitoring efforts. Monthly Methyl Bromide (MeBr) concentrations measured near Hudson Park in West Long Beach beginning January 12, 2023 are shown in the data dashboard below. Hover over the blue concentration data bars in the time series to see the concentration for that month. All reviewed data are available via CARB's AQView website. Hover over the single (*) or double asterisks (**) to find out more information.
What are the potential health effects of MeBr exposure?
Methyl bromide is a toxic air contaminant that can affect the respiratory and nervous systems. Exposure above the acute REL for one hour or more (acute exposure) can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and difficulty breathing, while exposure above the chronic REL over a long period of time, like a year or more (chronic exposure), may lead to lesions in the nasal cavity and other developmental and nervous system effects. MeBr is listed under Proposition 65 for potential reproductive harm.
For information on specific health impacts from MeBr, please see the National Pesticide Information Center’s fact sheet: http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/MBgen.pdf.
For information on pesticide-related illness and injury, please visit OEHHA’s Health Education Resources web page for pesticides.
How can I take steps to reduce risk if I live near the sources?
Breathing in low levels of MeBr over a long period of time (chronic exposure) is a concern for residents closest to the monitoring site. If you live near the monitoring site (close to Webster Avenue, between West Willow St and West Burnett St), and want to take a precautionary measure to help reduce risk of exposure, you can close your windows and doors during and after fumigation hours (between 6 pm and 11 pm) in the evenings when emissions may be highest (between February and the end of April).
If you think you have been exposed to a pesticide or you are experiencing symptoms, please call your medical provider. For free first aid advice, call Poison Control at 1-800-222-1222.
What agencies are responsible for regulating MeBr use and emissions in Los Angeles County?
In addition to annual restricted materials permits issued by the LA County Agricultural Commissioner, MeBr use is currently regulated through an interagency Memorandum of Understanding between the SCAQMD and the Los Angeles County Agricultural Commissioner (available here). Five agencies are responsible for regulating the use and emissions of MeBr at fumigation facilities: CARB, DPR, LA CAC, the South Coast AQMD, and U.S. EPA, as described below:
- California Department of Pesticide Regulation (DPR): State agency responsible for regulating pesticide use to protect human health and the environment and fostering sustainable pest management. Pesticides must be evaluated prior to registration for use in California. DPR continues to evaluate potential risks from registered pesticide by monitoring for potential exposures and illness cases.
- Los Angeles County Agricultural Commissioner (LA CAC): County agency responsible for issuing and enforcing permits for pesticidal use of MeBr in commodity fumigation and conducting site inspections. LA CAC permits can be conditioned by the CAC to account for local conditions and/or incorporate DPR recommended permit conditions for MeBr.
- California Air Resources Board (CARB): State agency responsible for identifying and regulating emissions of toxic air contaminants. Monitors air quality and sets reporting requirements for air pollutants and addresses local air pollution through the Community Air Protection Program.
- South Coast Air Quality Management District (South Coast AQMD): Local air agency responsible for implementing the Air Toxics “Hot Spots” Program and regulating sources of air contaminants and monitoring air quality.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA): Federal agency that approves and registers pesticide products for sale and specifies restrictions and requirements for use on product labels. U.S. EPA sets regulatory requirements for MeBr as an air pollutant that is a volatile organic compound and a hazardous air pollutant.
What has been done to address this issue?
In December 2024, the Los Angeles County Agricultural Commissioner beganworking with both facilities to update their restricted materials permits. The facilities voluntarily agreed to updated conditions to their permits to reduce risk from facility operations, including:
- Requiring larger fans and stacks (industrial chimneys or flues) to be at least 55ft high to disperse emissions higher in the air and less likely to concentrate at ground level where people live and breathe.
- Explicit requirement that no fumigation can be done during school hours.
- More stringent requirements to prevent ground level leaks, to ensure all MeBr is emitted through the stacks.
- Increased record-keeping requirements to allow for tracking use of MeBr with ground level-monitored results, to measure improvements over time.
- Staggering fumigations between different chambers in the facilities to allow more time for emissions to disperse between different chambers in the facilities to delay releases, which prevents higher combined releases from each facility.
CARB will continue to monitor for MeBr and track progress over time to ensure the new permit conditions achieve the purpose of reducing ground level emissions in the community.
Where Can I Get More Information?
For questions or more information about the facilities’ operations or the restricted materials permits, please contact the LA CAC: Michael De Los Reyes, mdelosreyes@acwm.lacounty.gov, Phone: 626-226-6085.
For questions or more information about the methyl bromide monitoring data, please contact: cam@arb.ca.gov.
For more information on pesticide-related illness and safety, please visit OEHHA’s Health Education Resources web page for pesticides.
