Rail Emission Reduction Agreements
Categories
Contact
1998 Locomotive NOx Fleet Average Emissions Agreement in the South Coast Air Basin (1998 MOU)
The 1998 Locomotive NOx Fleet Average Emissions Agreement in the South Coast Air Basin (1998 MOU), signed by CARB, Union Pacific Railroad (UP) and BNSF Railway (BNSF), aims to decrease the use of old and dirty diesel locomotives in the South Coast Air Basin. Under the Agreement, UP and BNSF agreed to operate locomotive fleets that “on average” meet a Tier 2 NOx emission standard, or 5.5 g/bhp-hr by 2010 (and through 2030). The Agreement provides State Implementation Plan (SIP) creditable emission reductions.
2024 Fleet Activity Data for the South Coast Air Basin
The graph below illustrates locomotive activity aggregated by engine tier that has operated in the South Coast Air Basin (SCAB) from 2010 - 2024 using data from UP and BNSF reported to CARB under the 1998 MOU.
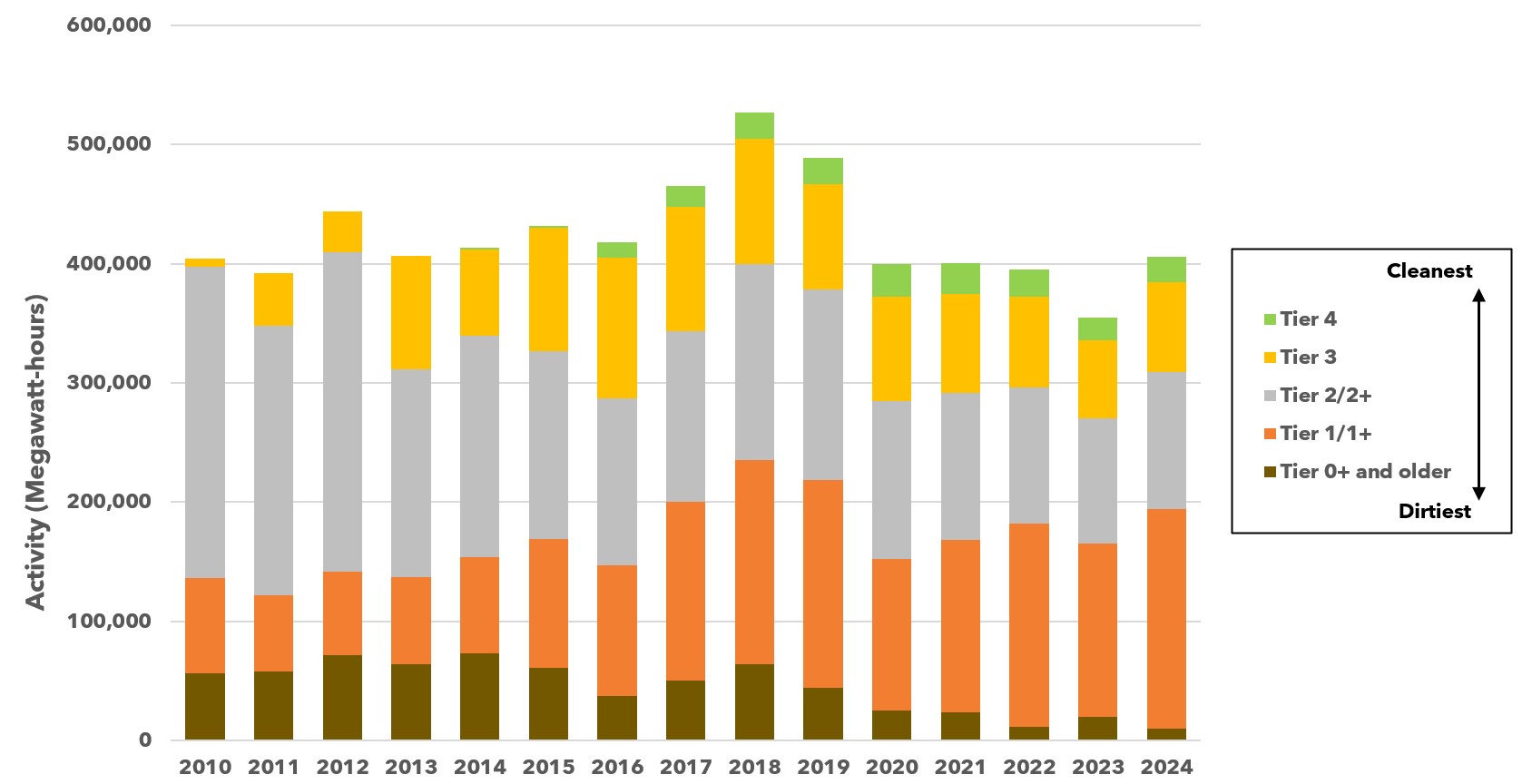
1. For more details, refer to the MOU summaries in the Archive of 1998 MOU Data below or contact us at locomotives@arb.ca.gov.
2. For more information on the U.S. EPA locomotive emission standards please visit Document Display | NEPIS | US EPA.
Union Pacific Railroad
Tier1 | Number of Locomotives2 | Megawatt-Hours (MWh) | % MWh by Tier | Weighted Average NOx Emission Level (g/bhp-hr)3 | Tier Contribution to Fleet Average (g/bhp-hr)4 |
Pre_Tier_0 | 11 | 73 | 0.0% | 9.1 | 0.00 |
Tier 0 | 251 | 5,286 | 2.6% | 8.0 | 0.2 |
Tier 1 | 1,909 | 102,502 | 51.3% | 6.7 | 3.5 |
Tier 2 | 1,215 | 52,412 | 26.2% | 4.8 | 1.3 |
Tier 3 | 805 | 29,406 | 14.7% | 4.9 | 0.7 |
Tier 4 | 230 | 10,188 | 5.1 % | 1.1 | 0.1 |
Total | 4,421 | 199,868 | 100% | 5.7 | |
ULEL credits used | 0.2 | ||||
Fleet Average | 5.5 |
1. For more information on the U.S. EPA locomotive emission standards please visit Document Display | NEPIS | US EPA.
2. Number of locomotives is the sum of all individual locomotives that visited or operated within the South Coast Air Basin at any time during 2024.
3. Many locomotives are certified to emission levels cleaner than the U.S. EPA emission standards or tiers. For the purposes of
this table, a locomotive’s actual certified emission level is grouped with the required tier level. Within each tier, the Weighted
Average NOx Emission Level is calculated by multiplying each individual locomotive's actual certification level by its
megawatt-hours of operation.
4. The Tier Contribution is calculated by multiplying the %MWh by Tier Level by the Weighted Average NOx Emission Level.
BNSF Railway
Tier1 | Number of Locomotives2 | Megawatt-Hours (MWhrs) | % MWhrs by Tier Level | Weighted Average NOx Emission Level (g/bhp-hr)3 | Tier Contribution to Fleet Average (g/bhp-hr)4 |
Pre_Tier_0 | 498 | 553 | 0.3% | 13.0 | 0.03 |
Tier 0 | 94 | 4,067 | 2.0% | 11.2 | 0.2 |
Tier 1 | 1,527 | 81,754 | 39.7% | 6.5 | 2.6 |
Tier 2 | 1,663 | 62,681 | 30.4% | 4.9 | 1.5 |
Tier 3 | 1,269 | 46,001 | 22.3% | 4.6 | 1.0 |
Tier 4 | 281 | 10,984 | 5.3% | 1.2 | 0.1 |
Total | 5,332 | 206,040 | 100% | 5.4 |
1. For more information on the U.S. EPA locomotive emission standards please visit Document Display | NEPIS | US EPA.
2. Number of locomotives is the sum of all individual locomotives that visited or operated within the South Coast Air Basin at any time during 2024.
3. Many locomotives are certified to emission levels cleaner than the U.S. EPA emission standards or tiers. For the purposes of
this table, a locomotive’s actual certified emission level is grouped with the required tier level. Within each tier, the Weighted
Average NOx Emission Level is calculated by multiplying each individual locomotive's actual certification level by its
megawatt-hours of operation.
4. The Tier Contribution is calculated by multiplying the %MWh by Tier Level by the Weighted Average NOx Emission Level.
2024 Compliance Report and Data Summaries
Archive of 1998 MOU Data
Previously Completed: The 2005 Statewide Railyard Agreement
The 2005 Statewide Railyard Agreement, which was completed in 2015, included a statewide idle reduction program, maximized the use of state and federal ultra-low sulfur (15 parts per million maximum) diesel fuel, and established a statewide visible emissions reduction and repair program. The agreement also required the preparation of 17 railyard inventories and health risk assessments.
