Some Products Emit Harmful Levels of Ozone
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) staff published a study about ozone emissions from 17 consumer products and home appliances. This study found that five products in three categories produced ozone at levels that may result in potential health effects.
Ozone is a reactive gas comprised of three oxygen atoms. While ozone high up in the atmosphere protects us from the sun's harmful rays, at ground level, ozone can cause adverse health effects such as coughing, chest tightness and shortness of breath. Exposure to ozone may both induce and worsen asthma symptoms and worsen lung disease; it might also increase the risk of premature death.
Study Findings
Products that were found to emit harmful levels of ozone included a residential ozone laundry water treatment appliance, two fruit and vegetable washers, and two facial steamers. Use of these products increased ozone concentrations in a small room to concentrations that exceeded the 1-hr California Ambient Air Quality Standard (CAAQS) level for outdoor ozone (0.09 parts per million [ppm]). The greatest increase in room ozone concentrations resulted from use of the laundry water treatment system. During one wash cycle, this product increased the room ozone concentration by an average of 0.11 ppm.
Due to users' proximity to this product, the concentration of ozone that users might be exposed to (or the personal exposure concentration) can be even higher than the room concentrations measured. Personal exposure concentrations that resulted from one use of some products tested are shown below. During one wash cycle, users of the laundry water treatment system may be exposed to an average of 0.42 ppm ozone potentially for 1 hour. This level of exposure is equivalent to about one-quarter to one-half of the ozone that a typical California resident may be exposed to in one day.
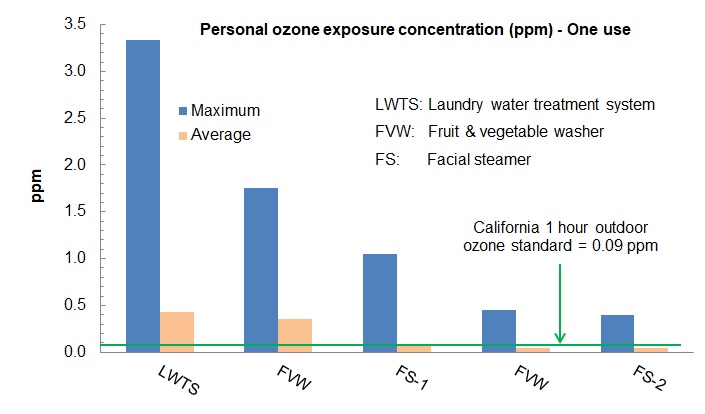
For some products, a single use did not increase the room ozone concentrations markedly, but repeated use can result in high personal exposure concentrations. For example, when a fruit and vegetable washer was used for three continuous wash cycles with reused water, the average personal exposure concentration was 2.55 ppm, over 28 times higher than the level of the 1-hr CAAQS. For the remaining products tested, their average ozone emissions were low, but high peaks were commonly observed. When using a facial steamer with an ozone-emitting ultraviolet (UV) bulb, for example, peak ozone levels as high as 1.1 ppm were reached. Such exposures may raise concerns for sensitive populations, such as people with respiratory diseases, and for those who use these products on a regular basis. It should be noted that most of the products tested in this study are used only briefly; thus, their impacts on indoor air quality and exposure are limited to shorter periods compared to continuously operating products such as ozone-generating portable air cleaners.
Ozone from Other Products
In addition to the products tested in this study, some air-cleaning devices have been found to increase indoor ozone concentrations to harmful levels. In September 2007, ARB adopted a regulation (California Code of Regulations, Title 17, §94800 - §94810) to limit the ozone concentrations from indoor air cleaning devices to no more than 0.050 ppm. More information about the regulation may be found on the fact sheet about the regulation.
Exercise Caution When Buying or Using Ozone-Generating Products
There are no consumer product regulations that limit ozone emissions from products similar to those tested in this study. Therefore, consumers should exercise caution when purchasing or using such products:
- Avoid using products that emit ozone intentionally. Read user manuals carefully to determine if a product can emit ozone. Some manufacturers explicitly indicate their products emit ozone, but others may use different words, such as "super oxygen", "super oxygenated", "saturated oxygen", "activated oxygen", "trivalent oxygen", "energized oxygen", "allotropic oxygen", "mountain-fresh air", or similar phrasing for ozone.
- Exercise caution when using products that may emit ozone as a by-product of their functions, such as products that have electrostatic precipitators, ionizers, corona discharge units, plasma generators, or UV bulbs. These products have the potential to generate high concentrations of ozone.
- If you still wish to use products that may emit ozone, only use them when the space is not occupied by people and has proper ventilation.
- Check the list of Potentially Harmful Ozone-Emitting Products, and avoid using these products, as they are advertised as emitting ozone.
More Information
For more information regarding this study, you may wish to view the fact sheet about the study. You can also read the article published in the journal Indoor Air for more detailed results. If you have any questions regarding this study or the information on this page, please email aircleaners@arb.ca.gov.
