Co-Processing of Biomass Feedstocks in LCFS
Categories
Background
Co-processing is a process where biogenic feedstocks are co-processed with petroleum intermediate products such as vacuum gas oil to produce renewable hydrocarbon fuels.
The biogenic feedstocks suitable for co-processing include upgraded pyrolysis oil, vegetable oil, used cooking oil and animal fat/tallow. Other feedstocks of interest may include lignin and sugars. Fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) and hydrocracking/hydrotreatment units in existing refineries are being investigated and utilized for co-processing. More than 75 percent of US refineries have FCC and/or hydrocracker units and hydrotreating units to process heavier distillate fractions. The US Department of Energy estimates that more than 8 billion gallons of renewable hydrocarbon fuels can potentially be produced from co-processing in existing FCC units in the USA. Research to date shows that co-processing of up to 20 percent (wt) biogenic feedstocks with vacuum gas oil (VGO) may be possible in FCC units. Co-processing can be a cost-effective option for utilizing existing refinery infrastructure to produce renewable hydrocarbon fuels. More importantly, co-processed renewable hydrocarbon fuels do not require additional investments in fuel distribution, storage, and dispensing due to their compatibility with existing transport and distribution infrastructures.
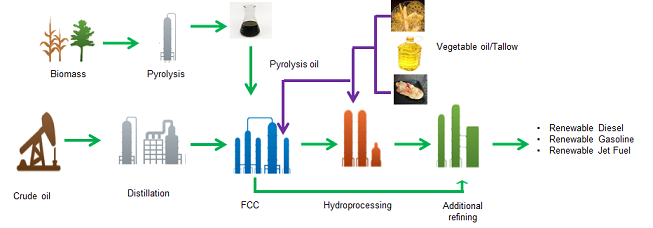
Interest in co-processing research and development and technology deployment is growing in recent years in response to climate change mitigation policies such as the California Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) and energy security concerns. Companies including Chevron, Ensyn, Tesoro and Petrobras, and research organizations/universities including the National Renewable Laboratory (NREL) and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) are actively working on research and development efforts. A recently registered prospective pathway involving co-processing of pyrolysis oil from forest residue shows that co-processed renewable diesel and gasoline can deliver more than 60 percent GHG savings. CARB recognizes the role co-processing can play in delivering low carbon hydrocarbon fuels to California and contributing to the 10 percent reduction target under the LCFS. EPA is currently updating the RFS2 to accommodate co-processing/bio-intermediates where biogenic feedstocks is partially processed at one facility and refined at another facility.
Co-Processing Technical Discussion Series
CARB is initiating technical discussions on co-processing beginning from December 2016. The co-processing technical discussions will include discussions led by CARB staff together with invited technical experts. The intent is to facilitate interested parties to provide inputs that will inform CARB on the quantification of renewable content of co-processed fuels and associated GHG emissions. The invited technical experts will provide presentations, relevant technical materials and participate in open discussions with interested stakeholders. The goals of co-processing technical discussions are:
- To gain a better understanding of co-processing via knowledge sharing, discussions and research collaboration among stakeholders. In particular, discussions will center on co-processing modelling and quantification of renewable hydrocarbon fuels and associated GHG emissions to inform the LCFS program.
- To identify technology barriers and potential solutions to co-processing deployment.
- To inform CARB and the general public on the potential of co-processing in meeting California’s climate goals and possible innovation and incentives for co-processing technology.
CARB will not attempt to produce any consensus documents from the co-processing technical discussions since the primary objective is to keep abreast of the best available information and understand the concerns/challenges related with co-processing.
The co-processing technical discussions will be accessible via webinar, teleconference and in person at CARB headquarters in Sacramento, California. If you have questions about the Co-processing Discussions, please contact Dr. Anil Baral at (916) 327-6913.
What's New
There will be total of 5 discussions beginning December 2016. The first co-processing discussion will be held on December 13, 2016 at CalEPA headquarters in Sacramento. The tentative schedules for technical discussions are listed in the table below. We will update the information once we finalize the dates and times for the remaining technical discussions.
Participating in Co-Processing Technical Discussions
Location: CalEPA Headquarters, 1001 I St, Sacramento, CA 95812
| Date and time | Room | Remark |
Kick-Off Meeting | December 13, 2016 Time: 8:30 am -12.30 pm | CR550 | Confirmed |
Technical Discussion I | February 7, 2017 Time: TBD | CR550 | Tentative |
To participate in the Kick-Off Meeting on December 13, 2016 by webinar: Register at https://attendee.gotowebinar.com/register/7260262573892437762
To participate by teleconference (please note that this is a toll call):
United States: +1 (213) 929-4232
Access Code: 972-711-783
References and Additional Information
- Ensyn biocrude receives CARB approvals for refinery coprocessing
- Research paper: Biomass derived feedstock co-processing with vacuum gas oil in FCC (Fogassy et al., 2010)
- Research Paper: Co-processing of waste vegetable oil and gas oil mixtures (Rana et al., 2013)
- Research Paper: Co-processing of upgraded pyrolysis oil (Mercader et al., 2010)
- Optimizing Co-Processing of Bio-Oil: Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) Presentation
- Refinery Integration of Renewable Feedstocks
- DOE Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) 2015 Project Peer Review
- Fast pyrolysis oil from pinewood chips co-processing with vacuum gas oil (Pinho et al., 2017)
