California Climate Investments provided more than $1 billion for underserved communities in 2019
Contacts
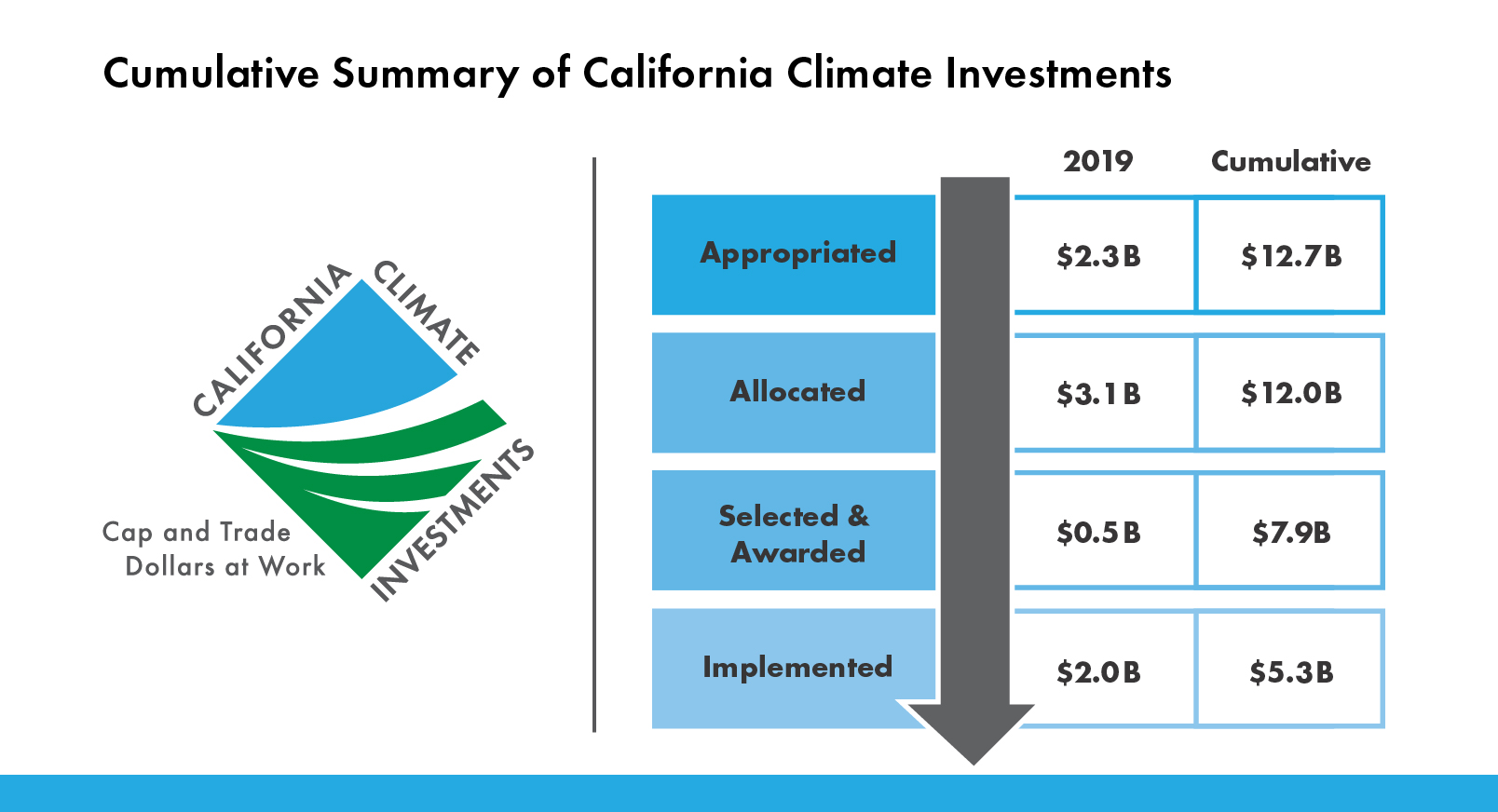
SACRAMENTO – 2019 was a record year for California Climate Investments with nearly $2 billion in projects implemented, including more than $1 billion to benefit disadvantaged and low-income communities.
The many benefits to Californians include improved public health, fire prevention, affordable housing and energy efficiency, as well as significant reductions in emissions of greenhouse gases. These benefits are described in the latest Annual Report to the Legislature on the use of auction proceeds from the state’s cap-and-trade program.
“The breadth and depth of the climate investment program help to reduce California’s greenhouse gas emissions, while benefiting every county in the state,” said CARB Chair Mary D. Nichols. “At the same time, these investments benefit the state’s most disadvantaged communities, those most heavily burdened by air and other forms of pollution. Projects in these neighborhoods reduce exposure to harmful air pollution and provide them – and all Californians – with more transportation options, cleaner air, increased energy efficiency and greener communities.”
Cap-and-trade auction proceeds are placed in the State Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund, then appropriated by the Legislature and distributed as California Climate Investments (http://www.caclimateinvestments.ca.gov) (CCI). That money is then awarded to individual projects selected by more than 20 different state agencies.

Lifting communities, addressing climate change
The projects funded so far are expected to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by almost 45 million metric tons of carbon dioxide during their lifetime. Projects implemented in 2019 alone will reduce GHG emissions by an estimated 5.7 million metric tons.
In addition to GHG emission reductions, investments improve community health because they promote active transportation, protect against dangerous heat, and reduce exposure to air pollutants that impair heart and lung health. Implemented projects with quantified air pollutant emission reductions are cumulatively expected to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOX) emissions by more than 20,000 tons and particulate matter (PM) emissions by 2,300 tons.
Disadvantaged and low-income communities will receive 57 percent of the benefits, substantially exceeding the 35 percent overall investment minimum required by law. This includes about 4,700 affordable housing units near transit, tens of thousands of water and energy retrofits, and cleaner trucks and cars in California’s most-polluted communities.
CCI projects in 2019 are estimated to support approximately 10,500 jobs within the state, across all sectors of the economy. Over time, these jobs will occur both directly through project implementation and indirectly by creating demand for goods and services in other industries. Investments also contribute to a just and equitable transition to a low-carbon economy through targeted workforce training and development initiatives.
For example, Transform Fresno, a project under the Transformative Climate Communities program, is implementing projects that will provide training and job placement for 200 local residents in low-emissions truck driving jobs and 120 local residents in welding jobs.
The SAFER Drinking Water Program will also receive ongoing funding starting with $100 million already disbursed in 2019. This money pays for planning, construction and repair of long-term sustainable improvements to drinking water systems in disadvantaged and low-income communities, increasing their resilience to climate change. This will help foster resiliency by ensuring that all Californians have an adequate and safe drinking water supply.
Reducing fuel, saving energy and protecting forests
New owners and lessees of low-carbon and zero-emission vehicles who receive incentives are expected to save 169 million gallons of fuel. Recipients of home solar installations and home energy-efficiency projects implemented by the Low-Income Weatherization Program are saving both money and energy because of these investments.
State-funded climate investments are also greening urban communities and contributing to forest health. Taken together, these projects will plant 13.2 million new trees. Other forest health and fire prevention projects include everything from fuel removal and forest management to new firefighting equipment and training for battling wildfires.
California Climate Investments attract additional investment. So far, $5.3 billion in implemented projects have leveraged an additional $21.7 billion, not including additional funding sources for the High-Speed Rail Project.
Examples include an $806,000 grant matched fully by Sun-Maid for an optimized compressed air energy system at its dried fruit packing and processing facility in the city of Kingsburg under the CEC Food Production Investment Program. The $29 million Forest Health Program's Redwoods Rising Project leveraged an additional $22 million from $7 million in initial CCI funding with participation of the Save the Redwoods League, the National Park Service, and State Parks. CCI also provided $4.7 million for an electric-vehicle carsharing project in partnership with the City of Los Angeles and Blue LA. The city provided $3.5 million. Blue LA provided $10 million, and an additional $13.5 million of in-kind contributions to expand the pilot, for a total project investment of $31.2 million.
CARB is also posting a new CCI data dashboard. The dashboard provides updates at a glance on how CCI dollars are being invested, and the many benefits of the various funded projects. The dashboard will be updated twice a year.
“We recognize that on this 50th anniversary of Earth Day, it is a difficult time for us all,” noted CARB Chair Mary D. Nichols. “The critical work of government continues even in the face of this unprecedented situation. Board members and staff at CARB are committed to advancing our clean air mission and our core values of service, accountability and excellence in everything that we do.”
